A lumbar puncture test or spinal tap is the process of extracting Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) from the lower end of the spine. The Cerebrospinal Fluid is a liquid that surrounds and cushions the brain and the spinal column.
Analyzing this liquid can help doctors detect the cause of diseases that affect the central nervous system.
The Lumbar Puncture Test As A Diagnostic Tool
The brain and the spinal cord are extremely sensitive parts of the human body. To protect them and to keep them functioning normally, they are surrounded by a membrane called the meninges.
Inside this membrane, a liquid called the Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) surrounds the spinal cord and the brain. This provides further protection, cushioning the region against any form of shock. The manufacture, re-absorption, and replenishment of CSF is a continuous process.
The body continually manufactures CSF from blood plasma. This CSF eventually gets back into the bloodstream and gets reabsorbed. Newly formed CSF replenishes the CSF lost through re-absorption.
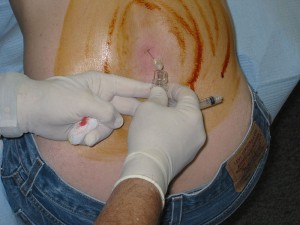
A Lumbar Puncture is the procedure for extracting CSF for analysis. After the lumbar puncture test is carried out, the composition of the CSF is studied for the diagnosis of various neurological conditions.
Local anesthesia is administered before the lumbar puncture test, and a small amount of CSF is collected through a needle. By attaching a thin plastic tube to the needle, the pressure of the CSF can be monitored. After gauging the pressure, the CSF that flows out through the hollow needle is collected in sealable test tubes. The needle is withdrawn when an adequate amount of CSF has been extracted. The fluid thus obtained is sent to the lab for analysis.
Why Do Doctors Tap Into The Lumbar Region?
The lower back or the lumbar region is chosen for a specific reason.
The spinal cord ends several inches above the lower end of the spinal canal. This leaves a space where the CSF can be extracted safely without risking the chance of an injury to the spine. This is mainly why doctors collect CSF from the lumbar region.
What Can A Lumbar Puncture Test Help Detect?
The Cerebrospinal Fluid is composed of proteins, glucose, and other components that can also be found in the blood. Studying the glucose level, the type of proteins, and the type of white blood cells in the CSF can help doctors identify infections and other conditions affecting the central nervous system. Some definite conditions that the lumbar puncture test can help diagnose are:
- Critical Infections: Fungal, viral, or bacterial, like Meningitis, Syphilis, and Encephalitis.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding in the region of the brain
- Cancers: Cancers of the brain or the spinal cord
- Inflammatory Conditions: Neurological inflammatory disorders like Guillain-Barre Syndrome and Multiple Sclerosis
Analyzing the CSF is the best way to detect diseases like meningitis, and for this reason, the lumbar puncture test is a vital diagnostic tool for detecting critical disorders and diseases of the central nervous system. Of course, the procedure must be preceded by proper lumbar puncture preparation measures so as to avoid any potential lumbar puncture side effects.