The bacteria named Mycobacterium tuberculosis are labelled as the main tuberculosis causes. This airborne infection spreads when the causative bacteria are transmitted through the tiny respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, sings, or talks. They can remain suspended in the air for long periods of time. If a healthy individual inhales this contaminated air, the bacteria enter his body through the respiratory system and lodge themselves in the person’s lungs.
Tuberculosis causes are aided by certain factors in the environment, such as small, enclosed spaces with inadequate ventilation. Rooms in which the air gets recirculated also enhance the probability of the infection spreading from person to person.
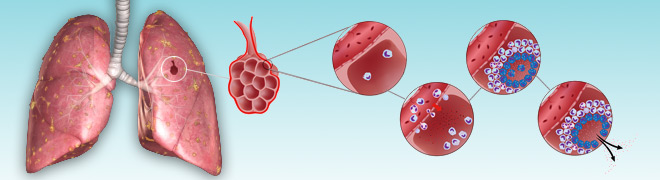
Tuberculosis Causes – The Mechanism Of The Tuberculosis Infection
The M. tuberculosis bacterium that causes tuberculosis requires a high amount of oxygen for growth and survival. That’s why it lodges itself in the alveoli, the deep pockets in the lungs, as these are rich in oxygen. Alveoli are the sites within the lungs where gas exchange takes place i.e. carbon dioxide is expelled from the blood and oxygen is added to it. Following the primary infection, the disease can stay in a dormant form or it can turn active.
In most people, a latent disease develops in which the immune system keeps the TB under control. Individuals carrying the latent form of the disease are not infectious and symptomatic, and a majority of them remain in good health. Later, when the immune system is weakened due to a variety of reasons, the tuberculosis bacteria can get reactivated and lead to the active form of the infection.
Tuberculosis Causes – Triggers That Causes An Active Infection
Some of the factors that can trigger reactivation of the disease are:
- Age
- HIV
- Diabetes
- Steroids
- Chronic poor health
Between 2 and 8 weeks after being infected with M. tuberculosis, a person’s immune system responds to the bacteria by walling off the infected cells. The alveoli in the lungs contain a particular type of immune cells called macrophages that fight the bacteria by engulfing them. But the fatty coating on the outer surface of M. tuberculosis protects them and prevents them from being killed by these alveolar macrophages. As the result, the bacteria remain intact within the cells. They grow and divide within the alveolar macrophages and are released when the macrophages die.
Latent TB Versus Active TB
While the M. tuberculosis bacteria remain trapped in the macrophages and continue to grow within them, the tuberculosis infection is said to be latent. The infected person doesn’t show any symptoms at this stage.
When the immune system is no longer able to fight and contain the bacterial population, the active tuberculosis infection is triggered. The symptoms of tuberculosis begin to manifest themselves at this stage. They include a severe cough with bloody sputum, fever with chills, profuse sweating at night, malaise, loss of appetite, and weight loss. This condition is called active TB.
Extra Pulmonary TB
A small number of the M. tuberculosis bacteria enter the bloodstream and travel to other organs like the spine, brain, bones, and the kidneys. This leads to extrapulmonary TB with symptoms based on the organ infiltrated by the bacteria.
Tuberculosis Causes – The Risk Factors Involved
Here are some of the risk factors that could trigger TB.
- Close and prolonged contact with TB patients
- Living in areas of poor sanitation and crowded housing
- Poor lifestyle choices, such as drug abuse, smoking, or alcohol abuse
- Chronic illnesses
- Age, very young and very old people are more susceptible to this condition than others
- Immunosuppression (for reasons like HIV, drugs especially corticosteroids, anti-TNFα agents, transplants)
- Diabetes
Tuberculosis (TB) is an extremely common and serious infectious disease. It has grown into one of the deadliest medical conditions in the world today. For this reason, it has become quite important to understand tuberculosis causes, its symptoms, and the tuberculosis treatment options available. More importantly, it is advisable to take solid precautions for tuberculosis prevention.