A liver function test can be used to identify any disease that interferes with the liver’s normal processes. Most diseases that affect the liver show very mild symptoms in the initial phases and it is important for you to get tested for these liver disease symptoms before they get worse or unmanageable.
According to a survey conducted by the United States CDC (Centre for Disease, Control and prevention), there are around 3.5 million people in the US alone who are infected with the hepatitis C virus, but more than 60% of them have no knowledge of the same.

A liver function test can be a liver blood test or a clinical test that’s carried out to see the stage of liver failure that the patient is going through. In other words, it is an indication of the state of a patient’s liver. These tests are usually used to:
- See if the patient has any liver disease present (or potential).
- Distinguish between the different disorders that cause liver damage.
- Note the extent of damage done to the liver.
- Set a course for the treatment based on the diagnosis.
Standard Panel for a Liver Function Test
Albumin
Albumin is the primary constituent of protein which is produced by the liver. It can be measured in an inexpensive manner. The secondary constituent of protein is Globulin, inclusive of immunoglobulin. The levels of Albumin recorded for patients suffering from chronic liver diseases are relatively low, like in the case of Cirrhosis.
In diseases like Nephrotic Syndrome, albumin is lost through the urinary tract and hence leads to a marked decrease in levels. If nutrition is poor or protein catabolism is impaired, which is the case in Ménétrier’s Disease, it leads to hypoalbuminaemia.
Alanine Transaminase
ALT is also known as Alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) or Serum Glutamic Pyruvate Transaminase (SGPT). It is an enzyme which is present in the liver cells called hepatocytes. When these cells are damaged, this enzyme leaks into the blood where its level is measured.
In case of acute liver damage the level rises exponentially. This happens in the case of paracetamol overdose or viral hepatitis. These elevations are measured to narrow down the possible list of causes behind liver damage.
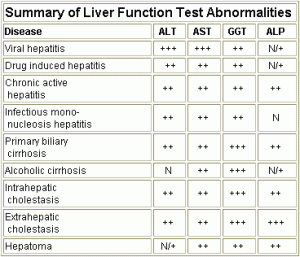
Aspartate Transaminase
AST is also called Aspartate Aminotransferase (ASAT) or Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase (SGOT). Like ALT, it is just another enzyme present in the parenchymal cells of the liver. It is not specific only to the liver as it is also present in skeletal and cardiac muscle and also in red blood cells.
Its levels are increased in cases of acute liver damage. As AST levels are not related only to the liver, its elevation does not always help in diagnosis. The ratio of AST to ALT however, is useful in determining the different causes.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
ALP is an enzyme present in the cells which line the bilary ducts of the liver. The levels of ALP in plasma are high when there is a large obstruction of the bile duct, infiltrative diseases of the liver or intrahepatic cholestatis. ALP is an enzyme which is also present in placental tissue and bones. As children’s bones undergo a lot of changes with time, its levels are generally higher in children.
Total Bilirubin
Bilirubin is a byproduct of the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is present in red blood cells. One of the liver’s functions is also to remove the Bilirubin from the blood.
An increase in total Bilirubin generally causes Jaundice and some other problems, namely:
-
Pre-Hepatic
Increase in production of Bilirubin pointing to internal hemorrhage and hemolytic anemia.
-
Hepatic
Deficiency in the metabolism of Bilirubin, which points to Viral Hepatitis and Cirrhosis
-
Post-Hepatic
Shows reduction in Bilirubin because of obstructions in the bile ducts.
Direct Bilirubin (Conjugated)
The patient’s diagnosis can be further narrowed by taking a look at the direct Bilirubin levels during the liver function test.
- If it is normal, then unconjugated Bilirubin is in excess and the exact location is before the excretion of Bilirubin. The suspects are Cirrhosis, Viral Hepatitis or Hemolysis.
- If there is an elevation in the level of direct Bilirubin, then the conjugation of Bilirubin will be normal, but the liver will be unable to excrete it. This happens in the case of either cancer or if gallstones obstruct the bile duct.
Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase
It is possible for GGT levels to get elevated due to a minor dysfunction from the liver’s part. This is generally raised when there is a high level of alcohol toxicity which points to Alcoholic Liver Disease.
Other tests that can be considered if liver function tests are not accurate are:
-
5 nucleotidase test
-
Coagulation test
-
Serum glucose
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
If any of these symptoms of liver failure are observed, it is recommended that you seek medical recourse immediately. Opting for a liver function test before any major symptoms of liver damage occur can be a good call as a liver transplant surgery or any other major medical recourse can be avoided this way.